Types of Rail Joints and Their Basic Requirements
What are the types of rail joints?

The joint formed between two rails, which incidentally forms the weakest part of the track, is called the rail joint. Many fastenings are found to move this joint as much as efficiently as possible. Depending upon the position of the joint or sleeper, the types of rail joints are classified as follows :
Types of Rail Joint According to the Position of Joint

Square Rail Joint :
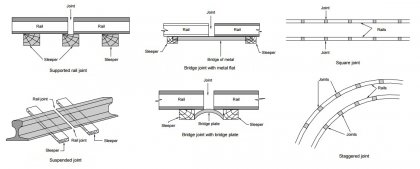
When a joint on one rail is exactly the opposite of a joint on another parallel rail, it is called a square joint. This type of rail joint is common in straight rails, but staggered joints are currently preferred.
Staggered Rail Joint:
When a joint in one rail is exactly opposite the center of the parallel rail length, it is called a staggered joint.Advantages of staggered rail joints:
- Centrifugal forces on curved tracks tend to push the track away from the straight line, and since the weakest part of the track is the joint, this effect appears before the joint.
- They reduce the tendency of centrifugal forces.
- It has been observed that staggered rail joints produce smoother running than square rail joints.
Types of Rail Joints According to Position of Sleepers

Suspended Rail Joint:
A rail joint located in the center of two consecutive sleepers is called a suspended rail joint. It is claimed that the load is evenly distributed over 2 sleepers, and when the joint is depressed, both rail ends are depressed. Therefore, they require more maintenance.
Supported Rail Joint:
When the sleeper is located exactly below the rail joint, it is called a support rail joint. This type of joint is not currently used. It is found from experience that the supported joint gives sufficient support with heavy axle load.
Bridge rail joint:
This rail joint is similar to a suspended rail joint. But in this case, a section of metal is used as a bridge to connect the ends of the two rails so that there are no bending stresses in the rails. To rest the bridge on two sleepers they are not heading out. But an experiment has shown that this type of joint is not possible in actual practice so presently it is not favored.Types of Rail Joints According to the Performance and Application
Ordinary Rail Joint:

That is, the coupling joint of two rails when the standard rail or non-standard rail is laid, and the splint and bolt are used to connect.
Compromise Rail Joint:

That is joints of different types of steel rails connected. To make the top surface of different rails and the inside of the head coincide, the corresponding special-shaped splint and special-shaped pad are used to connect. Special-shaped joints of positive line rails must use special-shaped rails.
Conductive Rail Joint:
a connector for conducting rail current or as a traction current loop, used in automatic blocking sections and electric traction sections. The inter-rail conduction coupling device is composed of two galvanized iron wires with a diameter of 5 mm, inserted into the round holes of the waist of the two rails - plug nail type, or welded into the steel sleeve at the head of the rail with a steel wire cable with a section of about 100 mm² - welding type.
Insulated Rail Joint:

It is also known as glued insulated rail joints. In the automatic blocking section, insulating joints are provided at the rail joints at both ends of the adjacent blocked section to ensure that the track circuit cannot pass from one blocked section to another blocked section. Generally, the insulated rail joint is to use a nylon rail header, nylon splint, and nylon bolt sleeve to separate the rail, splint, and bolt, so as to prevent the passage of current and play an insulating role.
Welded Rail Joint:

The joints formed by rail welding by resistance welding, small gas pressure welding, or thermite welding are mostly used for seamless lines.
Frozen Rail Joint (Rail Joint Bar, Rail Fishplates):
 |
 |
This joint is a frozen rail joint realized by increasing frictional resistance. Special crescent washers can be used to squeeze the bolt holes of ordinary rail joints. It is adopted that the rail joints should not be installed within the full length of the small bridge on the exposed bridge and within the temperature span of the steel beam with the rail expansion adjuster. The conditions for rail welding are not available. In the South of China, it is used to connect standard-length rails of ordinary lines into frozen long rail lines, which has received good results similar to welding long rail seamless lines.
Its characteristics are:
- It does not change the structure of the current joint.
- It does not use adhesives.
- It does not use additional mechanical parts.
- The joint resistance is high.
Expansion Rail Joint (i.e. temperature regulators):
AGICO Offers You The Requirements of Good Rail Joint:
- It should be strong, and stiff, and provide the same strength as the original track section.
- It should be cheap and durable.
- The rails provide a continuous and level surface for the movement of a train.
- It should maintain the gauge distance of the track.
- It should not allow the rail end to be battered in any case.
- It should be capable of maintaining the two rails at the same level.
- It should provide free expansion and contraction due to temperature.
- There should be easy removal and replacement of rail without disturbing the whole track.
- It should be elastic both laterally and vertically.
We receive enquiries in English, Español (Spanish), Русский язык (Russian), Français (French) and العربية (Arabic). Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!